Phase I: Normal Structure & Function
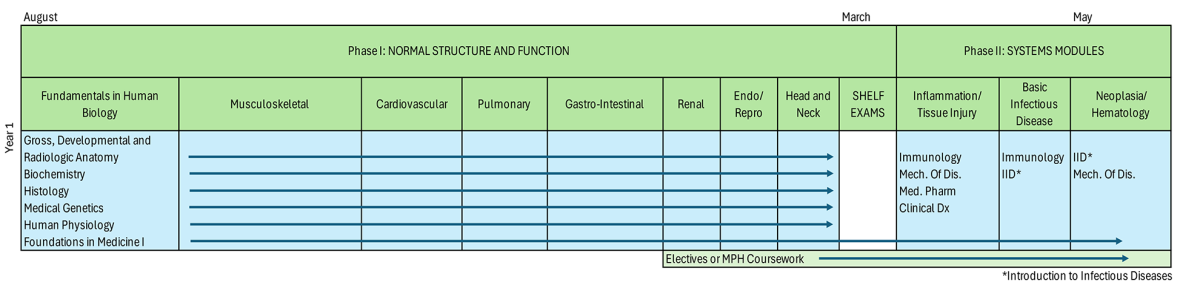
Focus – foundational basic sciences and introduction to clinical skills. Includes the following courses: Gross, Developmental, & Radiological Anatomy; Biochemistry; Histology, Medical Genetics, Foundations in Medicine I.
Modules
- Fundamentals in Human Biology: This module provides a foundational overview of human anatomy and embryology, with emphasis on the vertebral column, spinal cord, and key anatomical systems. It also introduces medical imaging, essential developmental processes, and core genetics concepts relevant to congenital anomalies and counseling.
- Musculoskeletal: Offers an integrated study of human structural and functional anatomy, emphasizing regional interrelationships among musculoskeletal, vascular, neural, and lymphatic systems. It also covers tissue histophysiology, muscle physiology, and endocrine regulation, linking foundational science to clinical relevance.
- Cardiovascular: Provides a systems-based exploration of cardiovascular structure and function, emphasizing histological analysis, hemodynamic regulation, cardiac physiology, and metabolic processes related to lipid and oxygen transport.
- Pulmonary: Provides a comprehensive study of the respiratory system, integrating principles of gas exchange, ventilation, acid-base balance, and respiratory mechanics with clinical correlations and embryologic development.
- Gastrointestinal: Offers an in-depth exploration of the gastrointestinal system, integrating digestive physiology, histology, and pathophysiology with genetics, metabolism, and medical imaging.
- Renal: Offers a comprehensive study of renal physiology, emphasizing tubular transport, fluid and electrolyte regulation, and the hemodynamic principles underlying glomerular function.
- Endocrine/Reproductive: Provides an in-depth study of the endocrine and reproductive systems, emphasizing hormone biology, organ development, and their clinical implications.
- Head & Neck: Provides a comprehensive study of the anatomy, histology, and embryologic development of the sensory organs and associated head and neck structures.
Phase II: Organ Systems Module
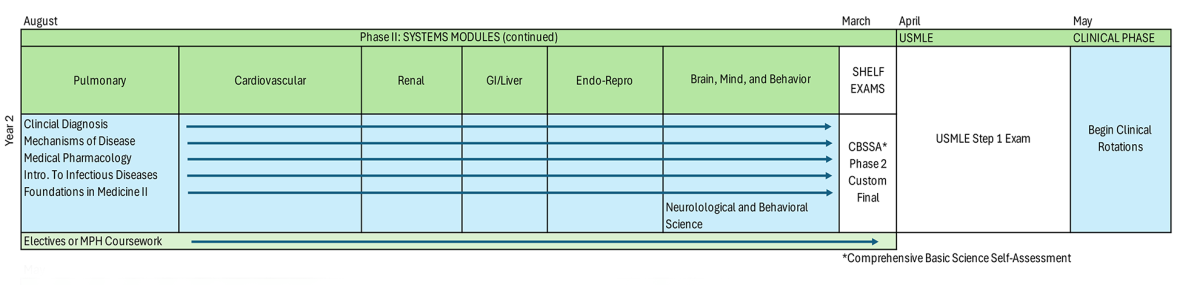
Focus – disease mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Includes the following courses: Immunology; Clinical Diagnosis; Mechanisms of Disease; Pharmacology; Introduction to Infectious Diseases; Foundations in Medicine II; Electives or MPH Coursework
Modules
- Inflammation/Tissue Injury: Offers an integrated study of immunology, pharmacology, and pathology, focusing on immune function, inflammation, autoimmune conditions, and related musculoskeletal diseases.
- Basic Infectious Disease: Provides a comprehensive introduction to the diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases, emphasizing microbial classification, laboratory diagnostics, and antimicrobial therapies.
- Neoplasia/Hematology: Provides a comprehensive study of neoplastic and non-neoplastic hematologic disorders, including their classification, pathogenesis, clinical features, and treatment strategies.
- Pulmonary: Integrates cardiovascular and respiratory pharmacology, infectious disease, and pulmonary physiology, emphasizing drug mechanisms, clinical diagnostics, and disease management.
- Cardiovascular: Provides a comprehensive study of cardiovascular pharmacology, pathology, and clinical care, integrating drug mechanisms, disease processes, and diagnostic approaches for a wide spectrum of heart and vascular conditions.
- Renal: Provides an in-depth examination of renal and genitourinary diseases, integrating pharmacology, clinical assessment, and evidence-based management of urologic and kidney conditions.
- GI/Liver: Provides an in-depth study of gastrointestinal, hepatic, and biliary diseases, integrating pharmacology, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical management of common and complex conditions.
- Endocrine-Reproductive: Offers an integrated study of reproductive, endocrine, and gynecologic diseases, emphasizing pathophysiology, pharmacologic treatments, and clinical reasoning through case-based learning.
- Brain, Mind, and Behavior: Provides an integrated study of neurology and psychiatry, combining foundational neuroscience with clinical skills in diagnosing and managing common neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Clinical Phase III (Year 3) Core Required Rotations
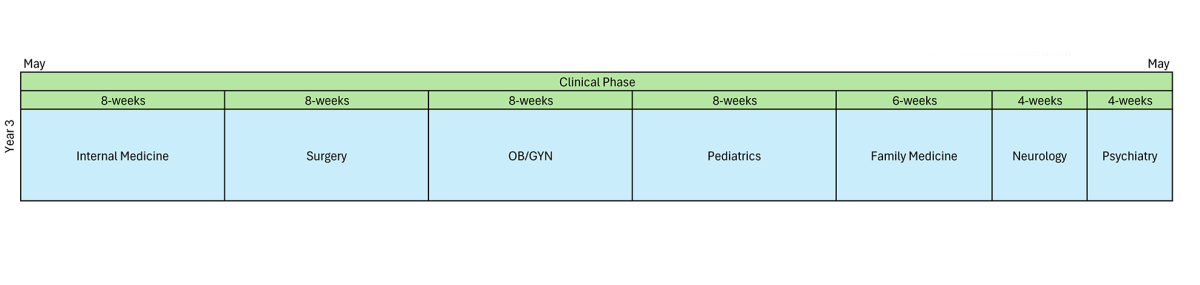
Focus - hands-on patient care in various (hospital and outpatient) clinical settings
- Internal Medicine (8 weeks): Students care for adult patients across a range of settings, including inpatient wards and outpatient clinics. Emphasis is placed on diagnostic reasoning, evidence-based management, and longitudinal care for complex medical conditions.
- OB/GYN (8 weeks): Students participate in the care of women across the reproductive lifespan, including prenatal care, labor and delivery, gynecologic procedures, and well-woman exams, with experience in both inpatient and ambulatory settings.
- Pediatrics (8 weeks): Students learn to assess and manage the health of infants, children, and adolescents through inpatient, outpatient, and newborn nursery experiences, with attention to developmentally appropriate care.
- Surgery (8 weeks): Students participate in the perioperative care of patients, with exposure to general and subspecialty surgical cases. Hands-on experience includes operating room participation, procedural skills, and post-op care.
- Family Medicine (6 weeks): Students are paired with a community family medicine physician to learn the essentials of family medicine through direct patient care. Students experience comprehensive primary care across the lifespan, including preventive services, chronic disease management, and health maintenance in diverse community-based settings.
- Neurology (4 weeks): Students develop skills in performing neurologic examinations and managing common neurologic disorders.
- Psychiatry (4 weeks): Students engage in the evaluation and care of patients with mental health conditions.
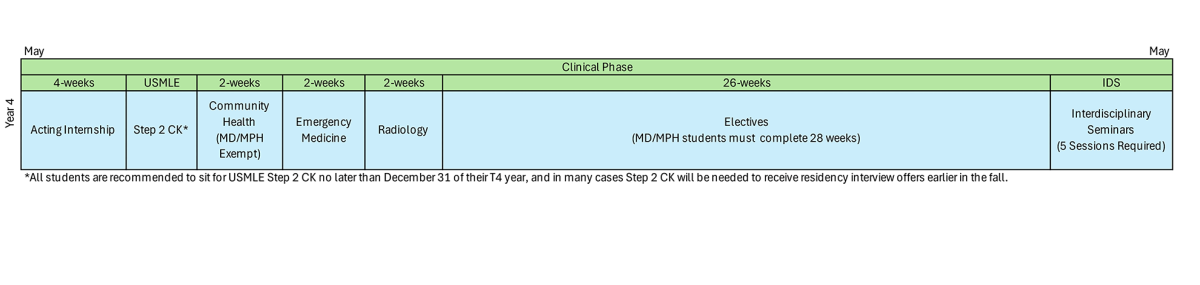
Focus - refining clinical skills and preparing for residency
- Emergency Medicine (2 weeks): Students assess and manage acute medical and trauma cases in the emergency room setting.
- Radiology (2 weeks): Students learn to interpret common imaging studies, understand appropriate imaging modalities, and integrate radiologic findings into clinical decision-making.
- Community Health (2 weeks): This rotation emphasizes population health, public health principles, and care delivery in underserved or community-based settings.
- Acting Internship (4 weeks): Students assume responsibilities similar to that of a first-year resident (“intern”), managing patient care under supervision in a specialty aligned with their career goals.
- Electives (26 weeks; 28 weeks for MD/MPH students): Students select rotations that align with their interests or intended specialty, providing opportunities for advanced clinical exposure.
- MD/MPH, MD/MBA, or MD/PhD tracks may include additional coursework or research
